What is Software Quality? and How to achieve it?
November 29th, 2023

Software quality is an important part of development because it shows how good and reliable a product is. It checks how well requirements are met, which affects how happy users are, how well the system works, and how successful the project is. To get high quality, you have to follow standards that cover more than just functionality carefully.
These standards cover things like reliability, security, and usability as well. This dedication not only meets but also goes above and beyond what users expect, which builds loyalty. Higher quality cuts down on bugs, which makes the system more stable and boosts user confidence.
Besides the immediate benefits, it makes maintenance easier, which lowers the Total Cost of Ownership. Software Quality Engineering (SQE) is very important. It uses methods and tools throughout the whole development process to make sure that standards are followed. On this journey, we promise to deliver value, build trust, and help the project succeed.
What is software quality?
Software quality is not just about ticking off technical requirements; it’s about creating software that empathizes with its users, anticipates their needs, and delivers value beyond expectations. It’s about crafting software that feels like a trusted companion, making life easier, more efficient, and more enjoyable.
When software prioritizes the user experience, it becomes more than just a tool; it becomes an enabler of progress, creativity, and connection. It eliminates frustration and empowers users to achieve their goals with ease.
Key aspects that conclude software quality include:
- Good Design: Aesthetic and user-friendly design is imperative to captivate users.
- Reliability: Software should flawlessly execute functionalities without glitches.
- Durability: In this context, durability refers to the software’s ability to function seamlessly over an extended period.
- Consistency: The software must perform consistently across platforms and devices.
- Maintainability: swift identification and resolution of software bugs, coupled with trouble-free addition of new tasks and enhancements.
- Value for money: Both customers and companies investing in the app should perceive the expenditure as worthwhile, ensuring it doesn’t go to waste.
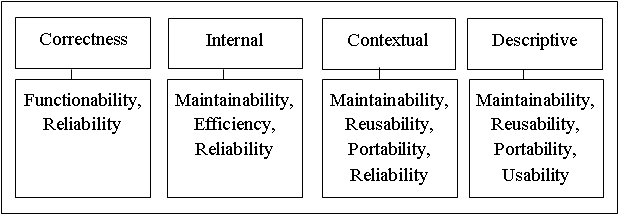
ISO/IEC 25010:2011 Software Quality Model
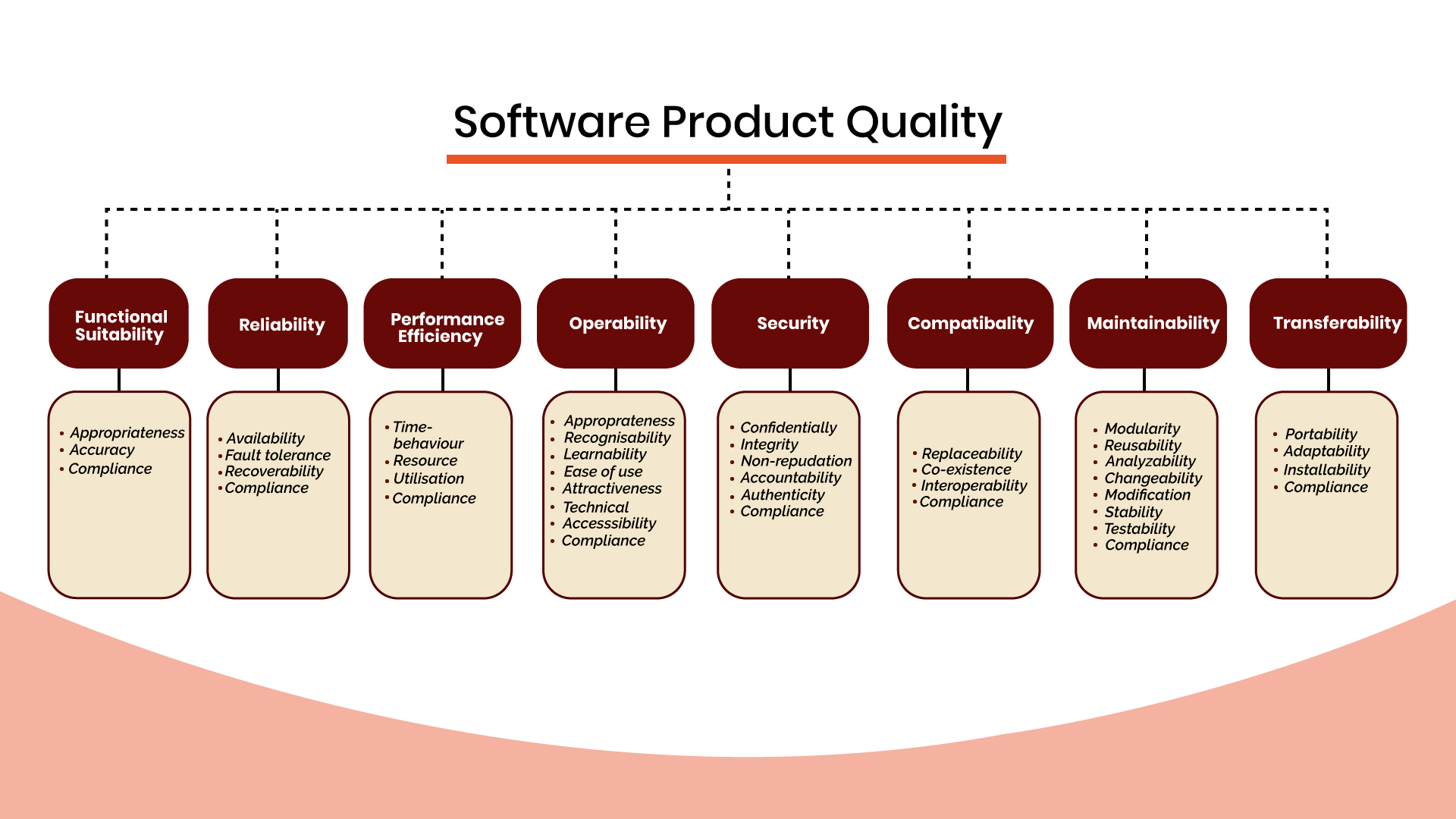
What is The Software Quality Model?
A Software Quality Model serves as a framework designed to assess the quality of a software product. It acts as a structured approach for evaluating various dimensions of software performance. Among the notable models, three widely accepted ones are:
- McCall’s Quality Model: A comprehensive model emphasizes eleven quality factors, including correctness, reliability, efficiency, integrity, and maintainability. McCall’s model provides a holistic view of software quality.
- Boehm Quality Model: Barry Boehm’s model focuses on qualities like effectiveness, dependability, integrity, usability, and maintainability. It provides a systematic methodology for assessing and improving the quality of software.
- Dromey’s Quality Model: Dromey’s model centers around six quality attributes, including functionality, reliability, usability, efficiency, maintainability, and portability. It offers a balanced perspective on software quality, considering various critical aspects.

Mc call’s Model
Mc Call’s model was first introduced in the US Airforce in the year 1977. The main intention of this model was to maintain harmony between users and developers.
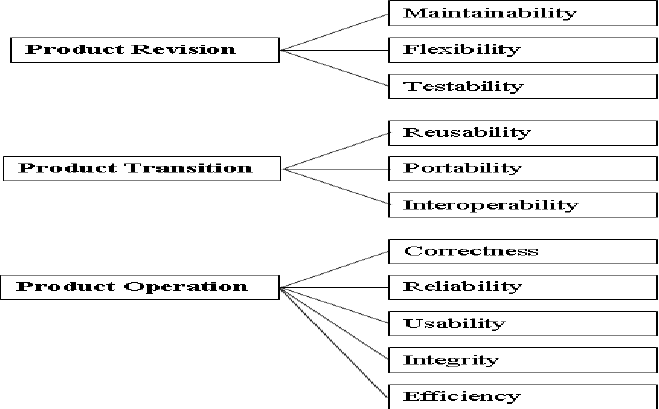
Boehm Quality Model
The Boehm model debuted in 1978. It was a kind of hierarchical model that was structured around high-level characteristics. Boehm’s model measures software quality on the basis of certain characteristics.
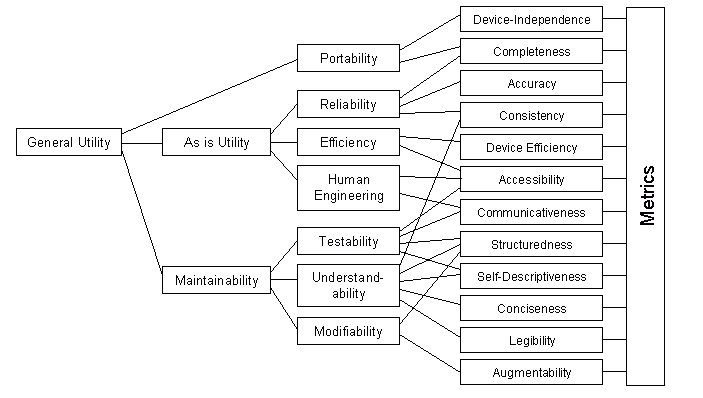
Dromey’s quality model
Dromey’s model is mainly focused on the attributes and sub-attributes that connect the properties of the software to the quality attributes
There are three principal elements to this model
- Product properties that affect the quality
- High-level quality attributes
- Linking the properties with quality attributes
How can software engineers acquire software quality?
Making sure the quality of software is high is a complex task that requires software engineers to think strategically.
Here is a new list of things that can be done to improve the quality of software:
Strong Plan for Management:
Make a detailed plan for quality assurance that covers the whole process. Define quality engineering tasks at the start of the project, making sure they fit with the skills of the team and the needs of the project.
Evaluation of the strategic team’s skills:
At the start of the project, do a thorough evaluation of the team’s skills. Find out where the team might need more training or knowledge to make sure they are ready to take on quality engineering challenges.
Channels of communication that work:
Set up clear ways for everyone on the team to talk to each other. Clear communication makes it easier for people to work together and makes sure that everyone is on the same page with quality goals and procedures.
Identifying problems ahead of time:
Set up ways to find problems before they happen throughout the whole development process. This includes finding bugs early on, integrating changes all the time, and using automated testing to find problems quickly and fix them.
Learning and adapting all the time:
Promote a culture of always learning. Keep up with the latest best practices, new technologies, and changing methods in your field so you can adapt and improve your quality engineering processes.
Integration of Automated Testing:
Automated testing should be built into the development process. Automated tests not only make testing faster, but they also make sure that evaluations are consistent and can be done again and again, which raises the quality of software as a whole.
Full-Service Checkpoints:
Set up checkpoints at important points in the development process. At these checkpoints, there should be thorough code reviews, testing, and quality checks to find and fix problems before they get worse.
Adding customer feedback:
Ask clients for feedback and use it as part of the development process. Client feedback helps improve the quality of software by giving developers useful information about what users want and how the software will be used in real life.
Keep an eye on and improve performance:
Set up tools and routines for monitoring performance all the time. Find possible bottlenecks or places where the software could be better, and then improve it so that it meets or exceeds user expectations.
Excellence in Documentation:
Stress the importance of carefully writing down the steps used to make and test software. Well-documented code, test cases, and procedures make things clearer, make it easier to work together, and make maintenance easier in the future, which improves the quality of software in the long run.
Best Practices for Security:
Best practices for security should be used from the start of the project. Deal with security issues before they happen by doing things like reviewing the code, checking for vulnerabilities, and following security standards.
Focus on the end-user experience:
In the quality engineering process, put the end-user experience first. Find out what the users want, test the software’s usability, and make sure it fits their needs and preferences perfectly.
Software engineers can strengthen their dedication to software quality by using these strategies. This will lay the groundwork for software solutions that are reliable, efficient, and focused on the user.
How do we achieve Software quality?
Achieving quality will ensure maximum profit for your software business. But the biggest hurdle is to achieve quality and here are some of the ways.
- Define characteristics that define quality for a product
- Decide how to measure each of that quality characteristic
- Set standards for each quality characteristic
- Do quality control with respect to the standards
- Find out the reasons that are hindering quality
- Make necessary improvements
Read also: Why Quality assurance is shifting to quality engineering?
What Are Software Quality Metrics?
In every software project, amidst coding endeavors, it’s crucial to pause and assess the correctness of the work and the effectiveness of the processes. Metrics, in the form of pointers or numerical data, play a pivotal role in understanding various aspects of a product, the development process, and the overarching project—often referred to as the three P’s (product, process, and project).
Why Are Software Quality Metrics Important?
Software quality metrics serve as vital indicators for product, process, and project health. Accurate metrics offer the following benefits:
- Strategic Development: Develop strategies and provide the right direction for the overall process or project.
- Focus Area Identification: Recognize specific areas that require attention and improvement.
- Informed Decision-Making: Make strategic decisions based on reliable and comprehensive data.
- Performance Enhancement: Drive performance improvements by identifying bottlenecks and areas for optimization.
Let us now look at some very important and most commonly used Software Quality Metrics and how they are helpful in driving better code
Defect Density
The initial gauge of product quality involves quantifying defects found and fixed. A higher density signals potential development issues, prompting proactive improvement efforts.
Defect Removal Efficiency (DRE)
Critical for assessing testing team effectiveness. DRE quantifies defects removed before production, aiming for 100% efficiency to ensure robust software.
Meantime Between Failures (MTBF)
The average time between system failures varies based on the application under test. Enhancing MTBF reduces disruptions, fostering software stability.
Meantime to Recover (MTTR)
The average time to identify, fix, and deploy a fix post-failure A lower MTTR ensures swift issue resolution, which is vital for maintaining system reliability.
Application Crash Rate
Crucial for mobile apps and websites, measuring crash frequency is an indicator of code quality. Lower rates signify resilient, stable software.
Agile-Specific Metrics
In the dynamic landscape, agile methodologies introduce metrics aligned with rapid delivery:
- Lead Time: Measures project or sprint kick-off to user story completion, reflecting overall development efficiency.
- Cycle Time: Focuses on task completion per user story, aiding in identifying development process bottlenecks.
- Team Velocity: Crucial in Agile/Scrum, gauging tasks or user stories completed per sprint Guides project planning based on team capacity.
- First Time Pass Rate (FTPR): Reflects agile principles of dynamic, fast, quality delivery. Indicates the percentage of test cases passing in the first run.
- Defect Count Per Sprint: Simple yet useful, it counts defects found in each sprint, providing insight into user story quality.
Conclusion
Attaining software quality is indeed a journey, not a destination. It’s a continuous process of refinement and improvement, demanding perseverance and a commitment to excellence. But the rewards of this endeavor are immense. High-quality software is like a loyal companion, providing unwavering support and stability for your business endeavors. It’s the foundation upon which you can build a thriving organization, one that delights customers, fosters innovation, and achieves enduring success.
Remember, achieving software quality isn’t just about technical prowess; it’s about empathy, understanding, and a deep appreciation for the needs of your users. It’s about crafting software that not only functions flawlessly but also resonates with people, making their lives easier and more fulfilling.
Embrace the journey of software quality, and you’ll unlock a world of possibilities for your business. Let your software be a testament to your dedication to excellence, a beacon of trust and reliability for your customers. Together, we can create software that truly matters, software that makes a difference in the world.


 Software Testing Events
Software Testing Events App Testing
App Testing Web App Testing
Web App Testing Game Testing
Game Testing Automation Testing
Automation Testing Load Testing
Load Testing Security Testing
Security Testing Performance Testing
Performance Testing Hire a Tester
Hire a Tester